Would you like to make this site your homepage? It's fast and easy...
Yes, Please make this my home page!
In this section you were introduced to the bacteria, the single-celled prokaryotic
organisms that make up the kingdom Monera. Bacteria are divided into four phyla:
Eubacteria, Cynobacteria, Archaebacteria, and Prochlorobacteria. Their shape often
identifies bacteria. Bacteria can also be identified by the way in which their cell wall
is colored by Gram staining.
Bacteria obtain energy in a variety of ways. Some bacteria are autotrophs, which use a
source of energy such as sunlight or chemicals to produce food (organic molecules) from
simple inorganic molecules. Other bacteria are heterotrophs, which cannot make their food
and instead obtain energy from the organic molecules that they eat.
The energy stored in food molecules is made available for use when the food molecules
are broken down. Bacteria use the processes of respiration and fermentation to release the
energy in food. Because bacteria release energy in various ways, their need for and
tolerance of oxygen also varies.
Bacteria reproduce by binary fission. Some bacteria also undergo other processes, such
as conjugation and spore formation. During conjugation, genetic material is transferred
from one bacterium to another, thus creating new combinations of genes. During one type of
spore formation, a bacterium encloses its DNA with a thick internal wall to form a spore.
The spore can survive harsh conditions that would kill the bacterium in its active form.
Bacteria fit into the world in many ways. For example, some bacteria help animals
digest their food. Some are used in food production and industry. Others convert nitrogen
gas into a form that can be used by plants. Still others break down dead material and thus
help recycle nutrients in the environment.
For each of the following sets of terms, determine the characteristic common to three
of the terms. Then identify the term that does not belong.
- spitilium, coccus, methanogen, bacillus:
- prokaryote, nitrogen fixation, saprophyte, symbiosis:
- Eubacteria, Cyanobacteria, Archaebacteria, Azotobacteria:
- cell wall, nucleus, flagellum, cytoplasm
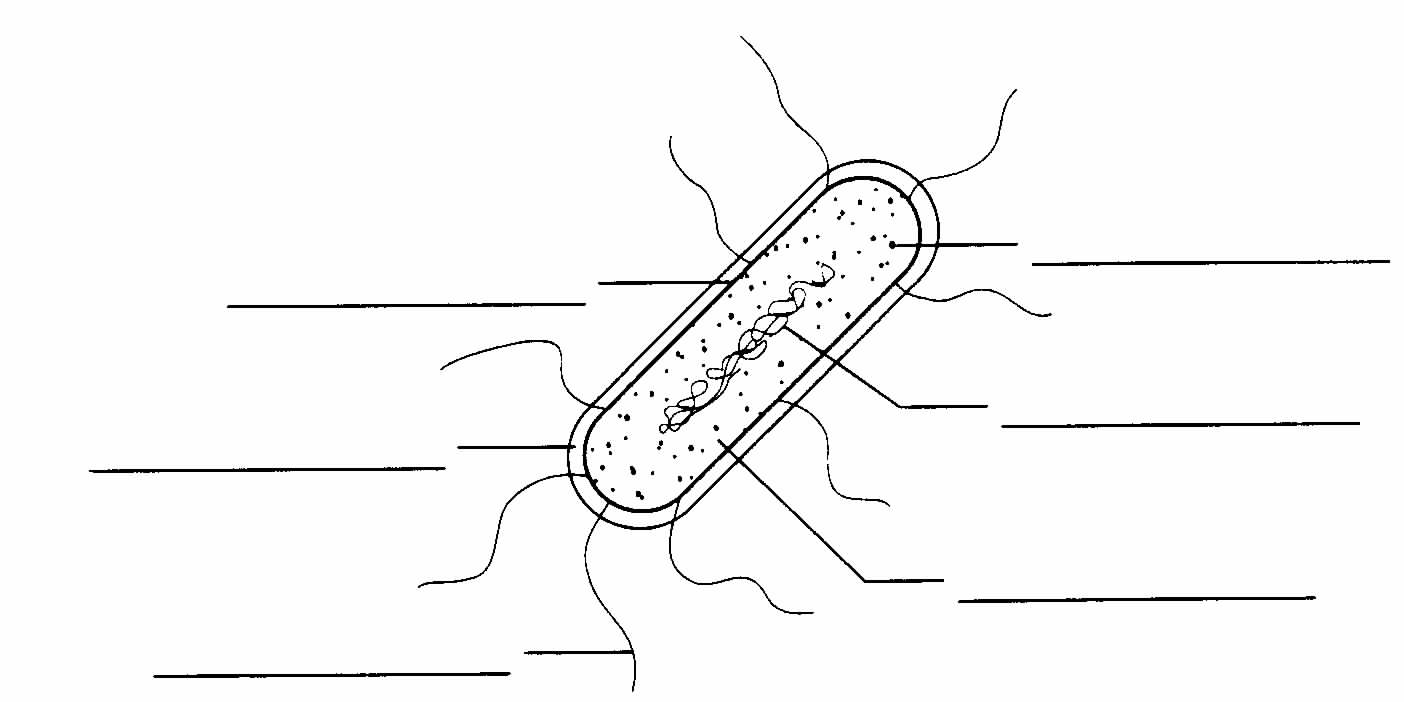
Label the diagram of a typical bacterium using the following terms: cell membrane, cell
wall, cytoplasm, flagellum, genetic material, ribosome
.
Then answer the questions that follow the diagram
.
- Is the bacterium in the diagram a bacillus, coccus, or spirillum?
- Explain. ____________________________________________________________
- How would you expect this bacterium to move?
- Suppose that this bacterium was a streptobacillus. What kind of colonies
would you expect it to form?
- __ are used in bioengineering research to change bacteria into new but
useful forms. [A]pili [B]cocci [C]plasmids [D]prophages
- _________ may have contributed to the development of our oxygenated
atmosphere.
- XXXX are used in bioengineering research to change bacteria into new
useful forms. [A]pili [B]cocci [C]plasmids [D]prophages
- a bacterium capable of growing in the presence of oxygen
- A close relationship in which both the bacterium and the other organism
benefit is _____.
- a deadly form of food poisoning.
- A piece of viral nucleic acid that has become part of the host cell DNA
is called a __. [A]plasmid [B]saprobe [C]prophage [D]bacteriophage
- a process used by some bacteria in order to use inorganic materials for
energy.
- A relationship between two species with both deriving benefit is called
[A]symbiosis [B]parasitism [C]conjugation [D]mutualism
- A rod-shaped bacterium is a __. [A]coccus [B]pilus [C]bacillus
[D]spirillum
- A round bacteria is a [A]bacillus [B]spirillum [C]coccus [D]pilus
- A spiral or curved-shaped bacterium is a __. [A]bacillus [B]spirillum
[C]saprobe [D]coccus
- a spore resistant to adverse environmental factors
- A streptococcus infection results from cocci bacteria that grow in _____.
- A structure in some bacteria that is resistant to adverse environmental
factors is a(n) __. [A]prophage [B]endospore [C]autotroph [D]saprobe
- A type of cell extension in bacteria is __. [A]cocci [B]pili [C]saprobes
[D]capsules
- A XXXX is a mass of cytoplasm in slime mold that contains diploid nuclei
but no cell walls or membranes. [A]filament [B]plasmodium [C]fragment [D]zygospore
- A(n) _?_ is a virus that infects a bacterial cell. [A]endospore
[B]decomposer [C]plasmid [D]bacteriophage
- A(n) XXXX are photosynthetic, a mass of cytoplasm that contain diploid
nuclei but no cell walls or membranes. [A]Sporozoa [B]green algae [C]acellular slime mold
[D]cellular slime mold
- Additional DNA in some Monerans is found in a(n) __. [A]capsule
[B]envelope [C]saprobe [D]plasmid
- All organisms are totally dependent on Monerans for [A]sewage
decomposition. [B]decay or organic matter. [C]nitrogen fixation. [D]their nutrients.
- All XXXX contain at least one of four different types of chlorophyll.
[A]algae [B]funguslike Protista [C]protozoan [D]parasites
- An external protective layer located on the outside of the cell wall of
some bacteria is a __ [A]coccus [B]capsule [C]pilus [D]vector
- an organism that breads down organic material.
- An organism that breaks down organic matter is a(n) __. [A]decomposer
[B]autotroph [C]consumer [D]producer
- an organism that depends on other organisms for a source of energy.
- An organism that derives its energy from dead or dying organisms is a(n)
__. [A]saprobe [B]mutualist [C]autotroph [D]bacteriophage
- an organism that derives its energy from dead or dying organisms.
- An organism that makes its own food is a(n) __. [A]autotroph [B]capsule
[C]pilus [D]vector
- An organism that requires oxygen to live is a(n) [A]obligate anaerobe
[B]lytic anaerobe [C]Lysogenic aerobe obligated aerobe
- Ancestral _?_ probably contributed a great deal to the development of an
oxygenated atmosphere. [A]Cyanobacteria [B]Archaebacteria [C]Omnibacteria [D]Schizophyta
- Ancestral XXXX probably contributed a great deal to the development of an
oxygenated atmosphere. [A]Cyanobacteria [B]Archaebacteria [C]Omnibacteria [D]Schizophyta
- Any organism or object that carries or transmits disease-causing
organisms is a(n) [A]capsule [B]pilus [C]prophage [D]vector
- Any organism that lacks a nucleus is in the kingdom _____.
- Bacteria are __. [A]consumers [B]viruses [E]producers [D]autotrophs
- T or F: Bacteria are found in only selected habitats.
- Bacteria are grown in sewage to produce each of the following except
[A]purified water. [B]toxins. [C]carbon dioxide gas. [D]products used in fertilizer.
- Bacteria may be [A]rod shaped [B]round [C]spiral [D]all of these
- Bacteria reproduce by dividing into two equal cells in a process called
- Bacteria reproduce sexually by _____.
- Bacteria take nitrogen from the air and convert it to ammonia that plants
can use by _____.
- Bacteria that break down dead organic matter are [A]parasites.
[B]saprophytes. [C]symbionts. [D]methanogen.
- Bacteria that can survive with or without oxygen are _____.
- Bacteria that require oxygen are called [A]obligated anaerobes
[B]obligated aerobes [C]lytic bacteria [D]Lysogenic bacteria
- Bacteria that stain red with Gram's stain must [A]be Gram positive. [B]be
Gram negative. [C]have protein outside the cell membrane. [D]have carbohydrate outside the
cell membrane.
- Bacteria that use complex molecules of dead organisms for energy are
_____.
- Cell walls in Monerans are weak and flexible.
- Conjugation in paramecia results in each individual being [A]identical
[B]haploid [C]fragmented [D]genetically altered
- Cyanobacteria carry out the light reactions of photosynthesis in their
[A]chloroplasts. [B]phycocyanin. [C]organelles. [D]membranes.
- Diphtheria and tuberculosis is caused by [A]streptococcus
[B]staphylococci [C]bacillus bacterium [D]rickettsiae
- Each of the following is true of Prochlorobacteria except that they
[A]are photosynthetic organisms. [B]live in the digestive tract of animals. [C]are
sometimes called Proclorophyta. [D]contain chlorophyll a and b.
- Euglenoids are similar to XXXX because they move using one or two
flagella for locomotion. [A]plants [B]animals [C]slime molds [D]sporozoans
- Fossil deposits of XXXX are used as "markers" to locate
potential oil deposits. [A]kelp [B]Foraminifer [C]Radiolarian [D]diatoms
- Genetic information can be exchanged between bacteria in a process called
[A]binary fission [B]vector analysis [C]mutualism [D]conjugation
- Halophiles can be found in __. [A]salty environments [B]areas without
oxygen [C]hot environments [D]cold environments
- If an organism is a one-celled prokaryote, it must be both a Moneran and
a (an) _____.
- Inorganic molecules used by chemotrophic autotrophs include hydrogen
sulfide gas. T F
- Many Protists in the form of XXXX are the food source of aquatic animals
such as whales.
- Moneran cell walls are [A]weak and flexible [B]brittle [C]strong and
rigid [D]lacking
- Monerans that are similar to green plants in that they trap the energy of
sunlight are [A]chemotrophic autotrophs. [B]phototrophic autotrophs. [C]chemotrophic
heterotrophs. [D]phototrophic heterotrophs.
- Nitrogen fixation involves each of the following except [A]soybeans.
[B]Rhizobium. [C]fertilizer. [D]nodules on roots.
- Nitrosomonas are chemotrophic autotrophs that use ammonia and oxygen to
produce energy. T F
- Organisms that do not use oxygen during respiration are [A]lytic bacteria
[B]obligated aerobe [C]Lysogenic viruses [D]obligated anaerobes
- Organisms that do not use oxygen during respiration are __. [A]lytic
viruses [B]obligate aerobes [E]lysogenic viruses [D]obligate anaerobes
- Photosynthetic bacteria that need organic compounds for energy are _____.
- Plasmids are used in X-ray research to change bacteria into new and
useful forms.
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever and typhus [A]streptococcus [B]staphylococci
[C]bacillus bacterium [D]rickettsiae
- Rod-shaped bacteria are spirilla. T F
- Sexual reproduction occurs in Spirogyra by means of [A]fragmentation
[B]mitosis [C]fission [D]conjugation
- Some Eubacteria move by means of [A]single cell membranes. [B]double cell
membranes. [C]flagella. [D]capsid.
- Spherical-shaped bacteria that grow in clumps or clusters are
[A]staphylococci. [B]streptococci. [C]diplococci. [D]bacilli.
- Sporozoans of the genus XXXX cause malaria. [A]Paramecium [B]Anopheles
[C]Plasmodium [D]Euglena
- Staph infections and boils are caused by [A]streptococcus
[B]staphylococci [C]bacillus bacterium [D]rickettsiae
- T or F: Cynobacteria enabled other organism to live.
- T or F: methanogen produce methane gas in the Great Salt Lake in Utah.
- T or F: Monerans are multicellular organisms
- T or F: Monerans are prokaryotes and have no membrane-bound organelles.
- T or F: The Archaebacteria may give clues about the early conditions of
Earth.
- T or F: The origins of bacteria and Cyanobacteria are difficult to trace
because of limited fossil evidence.
- The capsule is located inside the bacteria cell wall.
- The drug penicillin stops the formation of rigid walls in bacteria.
- The growth of bacteria is held in check by availability of food and
production of _____.
- The macronucleus is necessary for XXXX in paramecia. [A]sexual
reproduction [B]a sexual reproduction [C]moving the flagella [D]forming a zygospore
- The methanogen are a type of [A]Archaebacteria. [B]Eubacteria.
[C]Cyanobacteria. [D]Prochlorobacteria.
- The plant that produces more protein per acre than any other commercial
group is soybean. T F
- The term that includes all the others is [A]conjugation. [B]donor gene.
[C]recipient. [D]protein bridge.
- The term that is least closely related to the others is [A]interferon.
[B]virus. [C]Bacteriophages. [D]parasite.
- The XXXX are protists that have traits of both plants and animals.
[A]amoebas [B]ciliates [C]sporozoans [D]Euglenoids
- The XXXX produce between 70% and 75% of the Earth's atmospheric oxygen.
[A]protozoan [B]funguslike protists [C]prokaryotes [D]algae
This bacterium is a facultative aerobe. What process or processes would you expect it
to use to break down food? Explain.
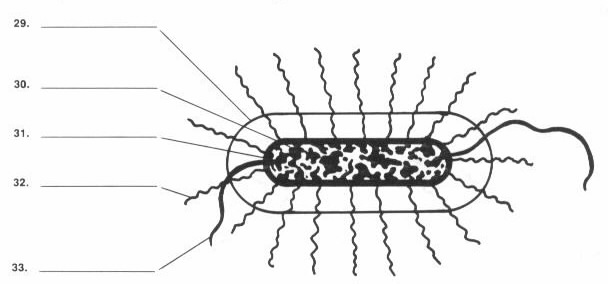
This bacterium is Gram-negative. What happens when it is subjected to Gram staining?
Throat infection and scarlet fever are caused by [A]streptococcus [B]staphylococci
[C]bacillus bacterium [D]rickettsiae
- Two types of cell extensions in bacteria are pili and flagella.
- Under a light microscope, bacteria that are Gram positive appear _____.
- Unlike all other organisms, bacteria that use sunlight for energy and organic compounds
for nutrition are [A]phototrophic autotrophs. [B]chemotrophic autotrophs. [C]phototrophic
heterotrophs. [D]chemotrophic heterotrophs.
- Virus or Moneran: a unicellular microorganism
- Virus or Moneran: cell wall made of long chains of polysaccharides
- Virus or Moneran: contains DNA or RNA
- Virus or Moneran: has an envelope
- Virus or Moneran: may have a mutualistic relationship
- Virus or Moneran: replicates after invading the host
- Virus or Moneran: replicates by binary fission
- Virus or Moneran: survives only as a parasite
- What does the capsule of a bacterial cell do? [A]it allows the bacterial cell to be
digested by body fluids. [B]It helps maintain water balance in the cell. [C]it exchanges
genetic information between bacterial cells. [D]It increases the rate of genetic mutation.
- When growth conditions become unfavorable, many bacteria produce _____.
- Which bacteria illustrate the wide variety of environments in which ancestral Moneran
forms may have existed? [A]Omnibacteria [B]Schizophyta [C]Cyanobacteria [D]Archaebacteria
- Which of the following bacteria is the cause of a common throat infection?
[A]staphylococci [B]rickettsia [C]Treponema pallidum[D]streptococcus
- Which of the following belong to the Omnibacteria? [A]Cyanobacteria [B]Prochloron
[C]Staphylococci [D]Halophiles
- Which of the following is not an evolutionary adaptation in bacteria? [A]They reproduce
rapidly. [B]They have a high rate of mutation. [C]They cannot exist under adverse
conditions. [D]They can utilize substances harmful to other organisms.
- Which of the following processes brings about an exchange of genetic information between
bacterial cells? [A]binary fission [B]mutualism [C]conjugation [D]replication
- Which virus infects Escherichia coil a bacterium common to the human intestine? [A]T-4
Bacteriophages [B]tobacco mosaic [C]Hepatitis B [D]herpes simplex
